It’s the most important destination for your brand and users. This is how to get there.
I had a prenatal massage at one of my favorite spa chains recently, and struggled with trust in a way I’ve never experienced before.
I love massages. I always have and I get them regularly. But a prenatal massage is different. You can’t lay down in the same positions or put pressure on certain body parts like the stomach and ankles. You feel stiff on the table, but because the hormone relaxin has actually loosened your joints, you may be far more flexible (and prone to strain) than you realize.
Overall, it’s like discovering yourself in a new body, which means I wasn’t in my favorite spa getting my 60 minute massage.
I was a new consumer buying a new service for the first time, and any trust accumulated between me and the brand up until that point had been wiped out. I was experiencing this with a fresh perspective.
Instead of zoning out the moment I laid down like I usually do, I was tense for the first 45 minutes before I could finally relax for the last 15. I simply couldn’t ease my body or turn my brain off.
I was unable to give myself over to the process because there weren’t enough brand interactions to get me to the tipping point of trust.
The brand had done nothing to indoctrinate me into our new relationship, and I had no way to frame the experience or contextualize what was happening.
Although the masseuse was well rated, kind and continuously checking in with me to make sure I was comfortable, I was missing the cues that should have told me, “this is what to expect”, “this is how you know it’s being done right”, and “this is what you should care about.”
Without those cues, I simply didn’t know when I could relax and I didn’t have the permission to let go.
The tipping point of trust is the moment that we go from thinking about an exchange to purely experiencing it. Depending on the business you are in and the customers you are speaking to, you can think of it as going from shopping to consuming, witnessing to being, or conscious to subconscious.
Users cross the tipping point when:
- they are willing to be vulnerable enough, and
- that vulnerability is rewarded.
Your job isn’t to get rid of the vulnerability. Vulnerability is an important relationship-building tool. Your job is to make that vulnerability worth it.
Trust is inherently tied to risk, but you don’t gain trust by making risk go away. You gain trust by making the risk worth it.
When you give people permission to be vulnerable and then reward them for it, you create a strong bond.
23andMe understands this. There is a great deal of inherent risk with their product, but instead of focusing on mitigating that risk in their brand positioning, they work to set a narrow field of expectation that users can measure their experience against:
When users take the leap and contextualize their experience not as a black box DNA test, but rather as “Meet Your Genes” — or put another way, a colorful way to familiarize yourself with anthropomorphized genetic personalities living in your body — they are rewarded with an easy understanding.
You know to interpret your results with a sense of playful discovery. You know to connect with your genes as if they are friends living inside of you. You know to see them not as cryptic markers that control your life, but rather as personified characters that answer to you when you ask them to reveal themselves.
That brand positioning primes you for a very different kind of experience.
(I‘ve written’ more about my own experience with this, and identity narratives in branding here.)
This also underscores something important: the tipping point is reached with the brand and not the UX.
Many people think that you get to the tipping point of trust with good UX moments or product features, but neither of those things can give users the context they need in order to have the right kind of experience going in.
They can certainly build trust incrementally, but they do not change the overall mindset of the user like brand can.
Brand is where you start.
The Nature of Trust and Control
Trust has been defined and redefined many times in the past few decades. It’s a tricky word to describe, like ‘cool’ or ‘porn’.
There is one recent definition, however, that works well in a branding context:
The willingness of a party to be vulnerable to the actions of another party based on the expectation that the other will perform a particular action important to the truster, irrespective of the ability to monitor or control that other party.
Mayer et. al., 1995:712
Trust means giving up control in one way or another, but in a user context, giving up control is scary. As brands, we work diligently against that fear, trying to offer control through transparency, dashboards, customization or any other number of features that put our customers in the driver’s seat.
On their own, these features fall short of true control because in the end, they’re just band-aids for the symptom.
No company can ever give 100% transparency. Dashboards are limited by definition. Customization usually only goes so far.
A far more powerful way around the trust issue is to change the way your user perceives control in the relationship to begin with.
23andMe moves the center of control from your genes (which comes from a very strong historical narrative, by the way, that says everything about a human is genetic) to you as an individual.
Genes are made to be coaches, HQ operators, friends and so on. They help, but they do not control us. They guide, but they do not command the quality of our lives.
For a silly brand campaign, it’s actually quite smart in changing perceptions of what genes are and how we should interface with them. Genes don’t control us. We do.
Control is in the perception. You can shift the center of control by shifting the paradigm.
Framing For The Tipping Point
Another way to think about the tipping point of trust is to think about framing.
Brands are framing mechanisms. They inform us how to embrace and internalize an interaction.
At the extreme end of the framing spectrum, we run into a bias called the framing effect. The framing effect is our predisposition to assume there are certain boundaries to a choice or situation, based on the information at hand:
The framing effect is a cognitive bias where people decide on options based on if the options are presented with positive or negative semantics; e.g. as a loss or as a gain.
People tend to avoid risk when a positive frame is presented but seek risks when a negative frame is presented. Gain and loss are defined in the scenario as descriptions of outcomes (e.g., lives lost or saved, disease patients treated and not treated, etc.).
As a former publicist, I can tell you this happens a lot in political reporting.
Take a look at the recent coverage for the Green New Deal and you’ll see that most of the headlines asked “Can we trust this deal?” rather than actually trying to understand what was in it.
The framing proved very powerful — from the beginning, we were primed to see it as problematic and unfeasible, even without knowing what it was comprised of.
You can literally watch hours of segments about the Green New Deal, as Vox reporter Carlos Maza did in the video below, and realize that none of them actually explain how the deal works:
Granted, the policy set forth was still lacking in certain details, but that’s not atypical for a proposal like this where further explanation is released later. There were plenty of details right there in the deal that were simply never covered in the press in any meaningful way.
Tactically framed political reports and articles are positioned so you don’t think to trust the content, you think to trust the critique.
Framing can be dangerous, especially when you have a lazy or jaded audience that’s become more accustomed to reacting than investigating.
But if framing can obscure the things that should matter, it can also force us to care about things that may have not mattered before.
Wilkinson Mazzeo PC is a small legal duo in San Diego, California that has used framing to completely change the way their customers view both the law and lawyers:
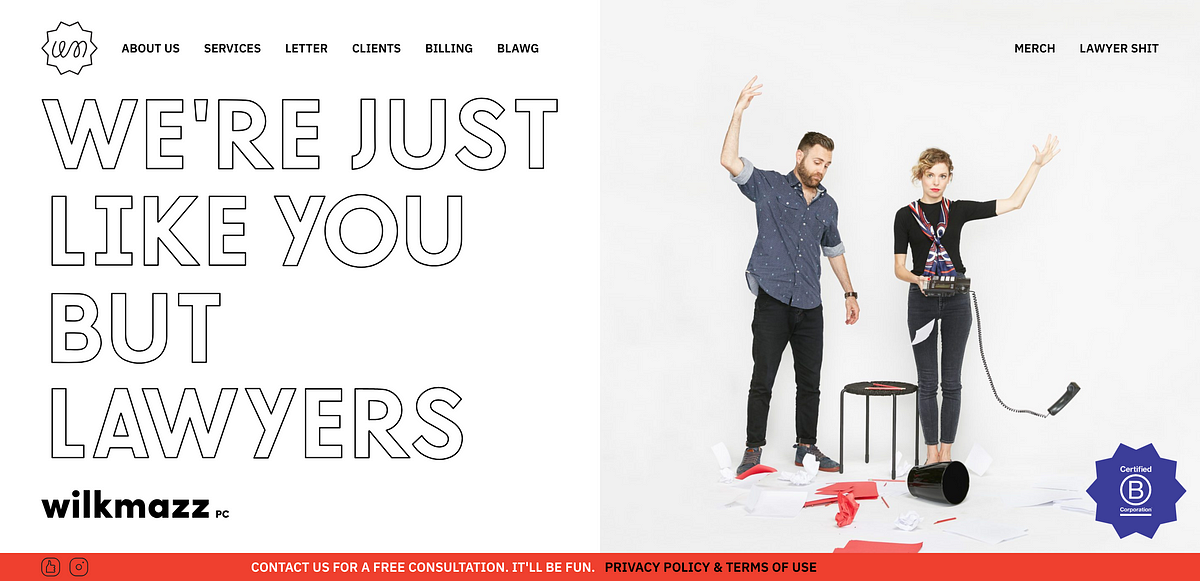
I often write about large brands in B2C or D2C, but this is a strong example of how the same branding principles can be applied to B2B, or smaller to medium-sized brands (although Wilkinson Mazzeo does have impressive clients experience under their belt).
As you go deeper into their website you realize this company is having a completely different conversation about law, entrepreneurship and community than anyone else in the space.
They say that they are “humanizing the practice of law”, but I would argue that even more importantly than that, they are reframing both what law should be, and what we should care about as consumers of that law:

You can’t explore this website as a creative or entrepreneur and not start having a conversation in your head. “Does my lawyer think like these guys do?” “Would my lawyer care as much?” “Is my lawyer creative enough to protect my company?”
“Have I been thinking about law in the right way this whole time?”
Emily Wilkinson and Sam Mazzeo have reframed the conversation to get you to the tipping point of trust very quickly. Whereas you may have observed the brands of other law firms in the past, you come to quickly experience the brand of this one right now.
They even have merch. They have merch because they know they’re not selling legal services, they’re selling a relationship based on trust.
Just like when you wear a Patagonia shirt or band tee, you’re celebrating your relationship with the other party.
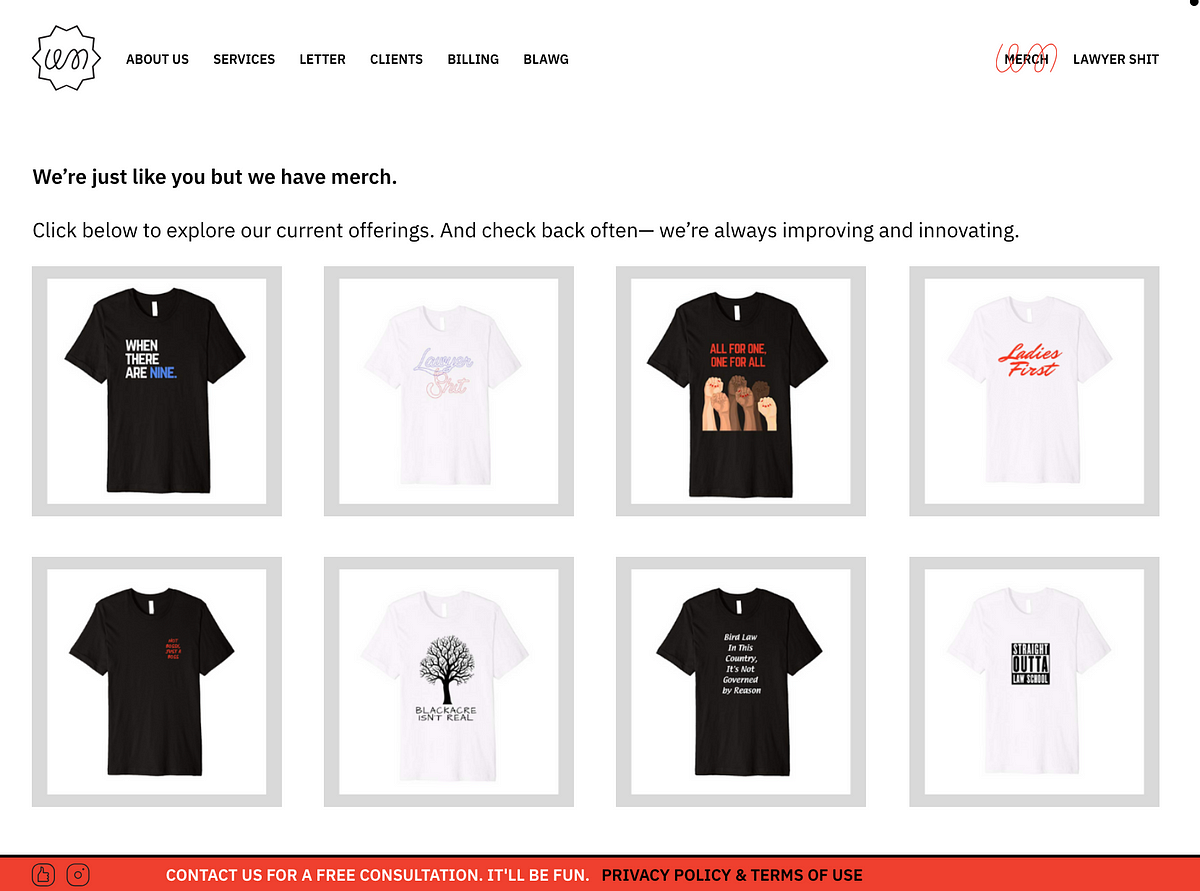
Most importantly, they make it easy to leave your biases about lawyers at the door when coming to this brand.
Framing for the tipping point of trust changes the reference points people use to gauge your brand.
Understand how to get users to the tipping point of trust first, then create the signals that will guide them there.
There is a certain kind of vulnerability required here in order to converse with this brand. You have to be willing to forget what you thought about lawyers. You also have to connect with these two specific lawyers as friends first, legal practitioners second.
Once you do, you’re rewarded for your vulnerability and start the relationship from a very different place.
That tipping point is the most important place to get to for this brand, or any other brand.
Find it and then steer your users toward it.




