If your users carry a shame story with them, you need a very different kind of strategy.
There are pockets of shame hiding in everyday life, and every one of your users encounters them.
Some of us feel shame about status symbols like money or marriage, while others may feel shame about personal shortcomings like fear or failure.
Shame is a universal part of the human experience, and is always borne of a story: stories we tell ourselves, stories that have been told to us, or stories we’ve co-opted from culture and community over time.
It’s also an important emotional trigger to study because unlike other triggers, it causes us to behave both irrationally and severely. There are few other things that sting us as deeply as a shameful memory, and no greater negative driver in our behavior. We’d go to great lengths to erase the cause of our shame if we could.
If a specific narrative makes someone feel devalued, wrong or guilty because of the expectations of their societal group, then it is a shame story.
Shame stories start to appear when our reality does not match what we feel is expected of us by others.
By that definition, they are intrinsically tied to the role we play in the group.
And when you look closely, you start to see that shame plays a role in many more industries than you may realize.
Some are obvious:
- Fertility (both male and female)
- Pain Management & Mental Health (cannabis, ketamine, suicide)
- Sex (less so dysfunction, more so pleasure and deviance… which is fascinating in its own right)
- Dating, Marriage (a woman’s worth as she gets older, a man’s worth based on his career/ height/ hair)
- Illness (especially when it’s terminal or dehumanizing, like cancer)
But some are not as obvious:
- Finance (money and self-worth are basically the same thing)
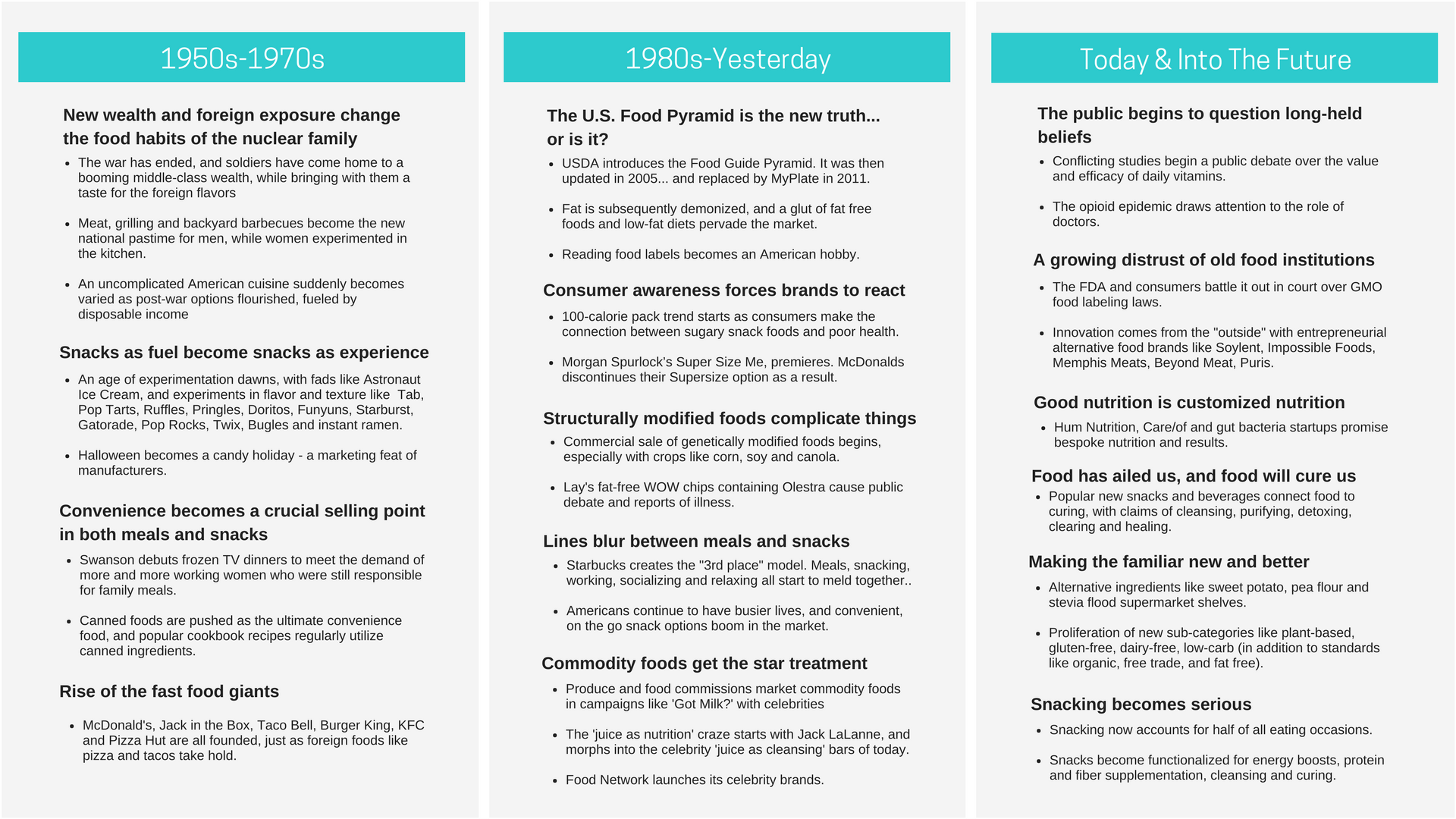
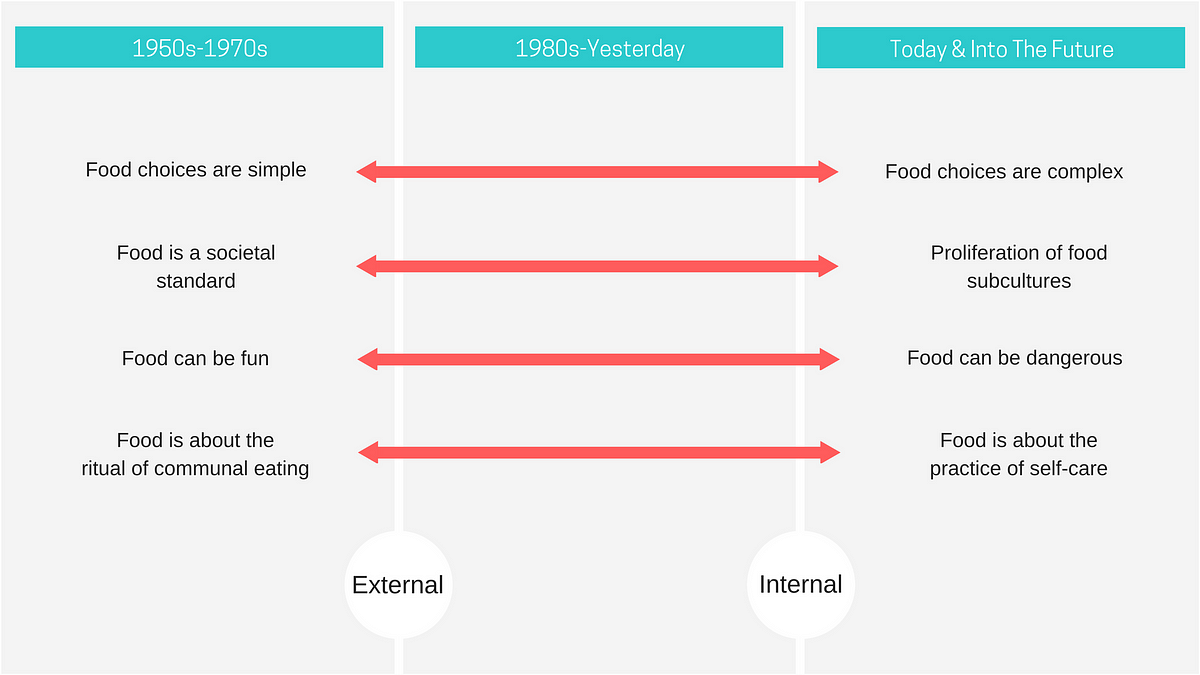
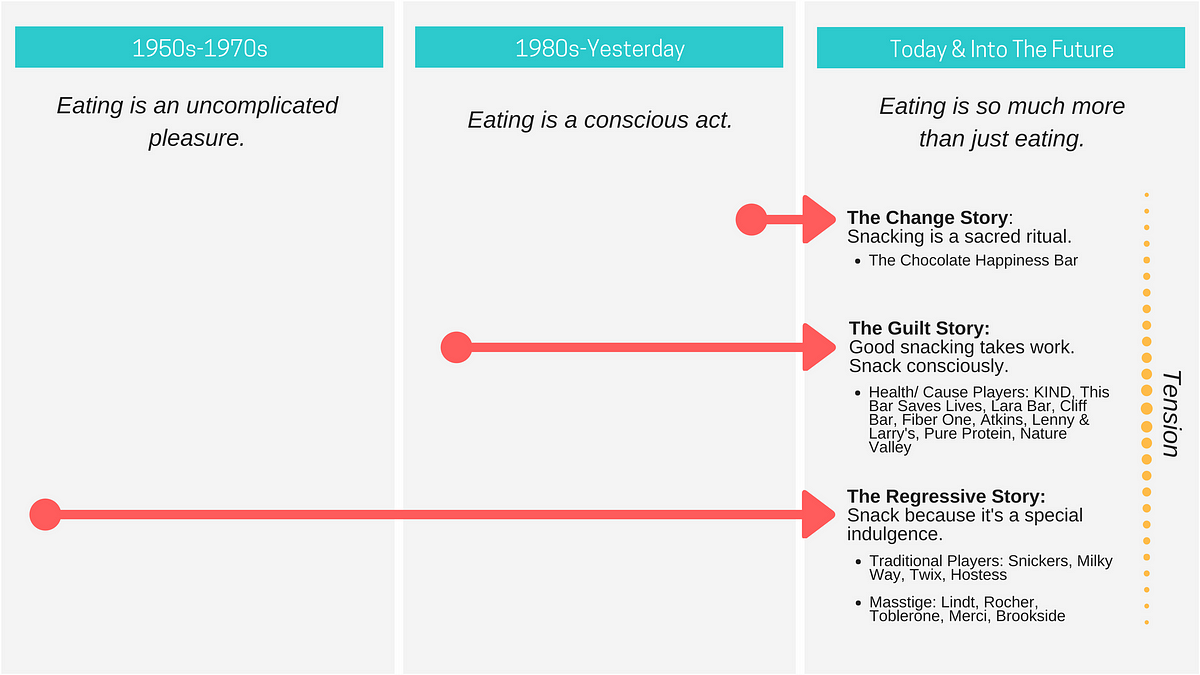
- Food (what we eat and how we eat is extremely personal, and a reflection of what we think we deserve)
- Parenting (the secret struggle between autonomy and giving yourself over)
- Beauty, Fashion (fitting a standard that is often classist, sizeist and racist)
- Higher Education (or lack thereof)
I call these stories dirty because as individuals, they make us feel wrong.
I call them ugly because as a society, we don’t want to look at them.
The next time you feel shame because someone cheated on you, or you refuse to leave the house because you’re ashamed of how you look, or you experience shame because you could not perform at work/ in bed/ as the breadwinner for your family, take note of its unparalleled power over your perception of reality. Even in the face of one hard fact —that none of these situations are your fault — you will continue to hurt yourself privately.
If your customers are fighting against a shame story somewhere in their lives that’s relevant to your brand, it wields the same kind of power over them, too.
You’re up against something very big and very strong, and you have to respect the different behavioral outcomes it creates. Fighting a shame story requires a different kind of brand strategy.
We see this as an increasingly important brand challenge because the low hanging fruit of structural disruption — access, supply chain, cost, distribution, etc. — has been exploited.
The next wave of disruption will happen on a cultural level, and shame stories are the structural dinosaurs living in our minds.
If you can effectively dismantle a limiting narrative for your audience, you can create a new reality for them… and creating a new reality is the ultimate goal of branding.
A new reality means new behaviors, new truths, and new opportunity for your company to speak to your audience.
Don’t just expose it. Replace it.
The hardest thing about shame is that we hide it.
Guilt is something we confess or share, but shame is something we work hard to conceal:
Shame is often confused with guilt — an emotion we might experience as a result of a wrongdoing about which we might feel remorseful and wish to make amends. Where we will likely have an urge to admit guilt, or talk with others about a situation that left us with guilty feelings, it is much less likely that we will broadcast our shame.
The very nature of its secrecy leads to a different set of behaviors.
People who feel shame over things like addiction, bullying or failure can project it in blame and anger… oftentimes even rage.
Others find ways to make themselves small in an attempt to ‘disappear’.
If you’re a CEO or strategist seeing these behaviors in your audience, it can be incredibly easy to read them the wrong way.
A nootropics brand founder might see an over-indexing of bro-culture on their platform and interpret it as bonding, or a the founder of a beauty brand might see its female customers hesitating to use bolder products and interpret it as lack of confidence, and they’d both have a good chance of being wrong.
Unlike other emotions, shame thrives the most when it remains hidden.
A lot of brands in the fertility space know this.
Many, like Modern Fertility, Glow, Extend Fertility, FertilityIQ and Dadi have worked to start an open conversation around the topic for both men and women.
It’s clear from their messaging, product bundling and brand stories that they want to start a discourse around something that has historically stayed behind the closed doors of a physician’s office.
I commend them for that.
What’s missing however, is a new story.
Shame stories don’t die just because they see the light. They die when a new story supplants them.
Shame is a weed, and one of the best ways to stop a weed is to grow something else in its place.
Unfortunately, old fears and biases don’t get erased simply because we talk about them and make them more normalized. They go away when they are written over with something else.
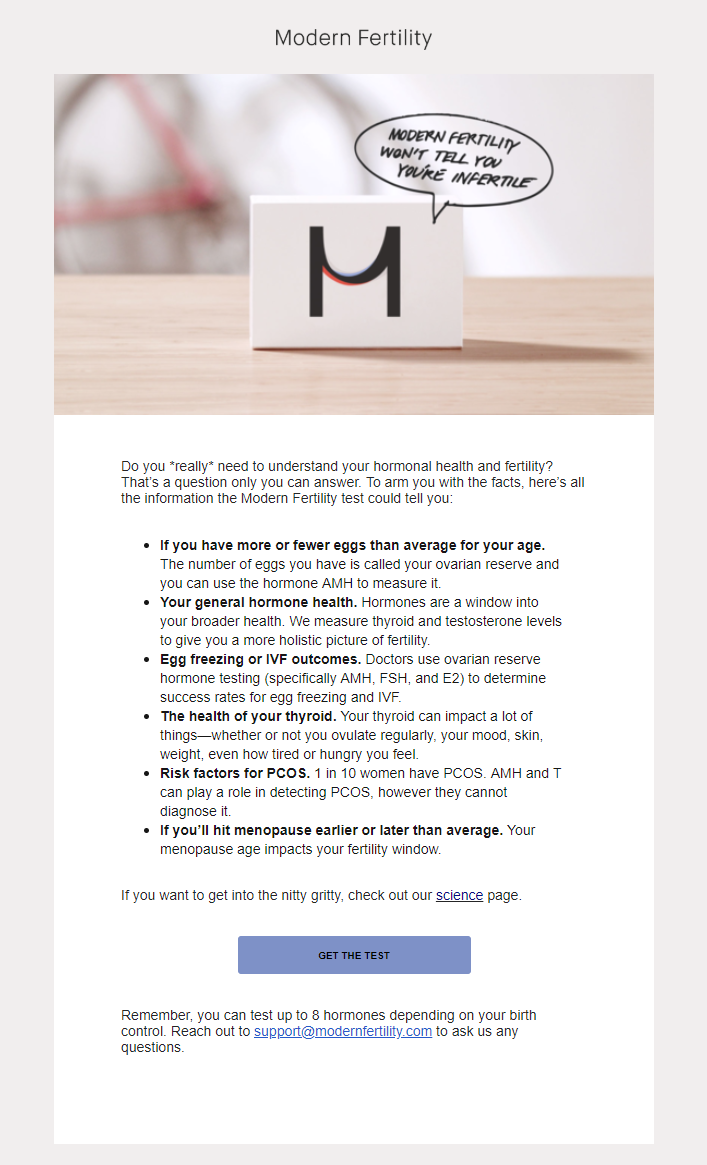
Messaging like “The very best information you wish you never needed” or “We won’t tell you you’re infertile” are not new stories.
They are versions of the same fear-based, private shame stories women have carried all of their lives, only now made public.
True, these brands are giving men and women new, democratized options for accessing the tests they need, without the gatekeepers that may have deterred them in the first place… but there is a much bigger brand opportunity to be had here.
Couples are ready for a new story that will replace the old one. They’re just not hearing it yet. Until they hear it, the shame (and its behaviors) will persist.
Women’s fertility startups seem to think that the problem they need to disrupt is one of price and access. What they really need to disrupt is the story of fear, shame and female identity. That’s a much harder business problem and I don’t see anyone tackling it.
— Jasmine Bina (@Jasmine_Bina) March 25, 2019
An adjacent industry that is successfully supplanting and old narrative with a new one, however, is sex.
Kill the old audience.
Just like fertility, sex used to live behind a gatekeeper (underground sex shops and far corners of the internet). Just like fertility, it could cause both great pain and great happiness. And just like fertility, it was a vessel for all kinds of shame that few would talk about.
Even as we move into a new era of female-forward sex brands and body positive movements, sexual health has been regarded as a fringe concern. You might not feel embarrassed to walk into an Adam & Eve, but you’re not going to talk about the details of your sex life with your yoga class either.
But that’s changing.
When sex toy company Dame Products launched in 2014, the founders realized that their audience overlapped more with a yoga crowd than with a traditional sex/ pornography crowd. When they saw that, they decided to position the brand squarely in the wellness space.
View this post on Instagram
View this post on Instagram
Wellness is an empowering narrative that stands tall in the face of anything shame-based. Consistently, throughout every touchpoint in the UX, both on brand properties and off, Dame communicates this new wellness story in different ways.
They make no secret of the “pleasure gap” they doggedly seek to close, have an active Dame Labs that invites users to join their people-centered research (regardless of gender or sexual identity), and most importantly, employ very clear design thinking because “we felt our products should look like beauty tools.”
“Everything in the world is about sex except sex. Sex is about power.”
-Oscar Wilde
As a result, sex toys like theirs were taking up space on shelves typically reserved for beauty, health and fitness.
As Business of Fashion pointed out last October, Dame was a signal that sex-care is the new self-care:
Sexual wellness is shaping up to be the next big opportunity in a category increasingly focused on wellbeing and ritualistic me-time. […]
It helps explain why US pharmacy chain CVS sells a rather stunning assortment of 48 whirring options — merchandised next to straightforward sexual health products like condoms and pregnancy tests — and family-friendly Target stocks 74 different models. Talk about self-care.
What Dame and others did was not only replace the old story with a new one (which in itself is remarkable), but they effectively moved the discussion from a group of people in the sex industry to a group of people in the self-care space.
They killed the old audience. Instead of having a hush-hush conversation about sex with one group, we were having it with another… our yoga friends.
The most important part of the shame equation is the group. Without the group to measure ourselves against, we would not feel shame.
The group is part of our social survival. They bind us, and our behaviors, to the people we care about, and reveal just how hyper-aware we are of how others perceive who we are to them.
If brands are tribal experiences, then shame lives somewhere within that tribe.
But if you kill the old tribe and create a new one, the equation falls apart. A new story can thrive someplace more fitting.
Give it the time it deserves.
Shame stories, just like shame itself, take time to dissipate.
They’re always old narratives.
They’ve been around for generations, long before your brand came on the scene. People may want to give them up but it’s scary to change your personal truth overnight.
However without fail, positive stories win in the long run. As a strategist, I’ve always believed this:
You will always have the choice to go positive or negative in your strategy. Tell the scary, shame-based story or the positive, goal-oriented story. Neither is inherently wrong, but some do work better than others.
Charity, global warming, war — why do none of these narratives work to permanently move people? Because they’re shame based. They inspire guilt. They create a feeling that may motivate in the short term, but most people want to avoid and escape in the long term.
But giving it time doesn’t mean just waiting for time to pass.
It means constantly telling and retelling the new story in new ways, and never letting the dust settle on the new reality you’re creating.
It means killing off the old audience over and over again, no matter how many times you have to do it.
Addiction, mental health, illness, marriage and dating — brands have been trying for years to change these stories, and the ones that will succeed are the ones that keep making noise.
When people start waking up, it will be the persistent brands who are there to meet them.
Giving it the time it deserves means using that time wisely. You can create a safe space that gently nudges your user in a new direction, and gives them the room they need to start changing the story for themselves.