Gone are the highfalutin ideals, goals, and visions that guided corporate social responsibility (CSR) since it became a strategic imperative in the early 2000’s. While initially innovative, it became easy for consumers to call this kind of CSR greenwashing, wokewashing, pinkwashing, etc. If you could name it, you could wash it.
At its most cringe, this era of CSR produced a cottage industry of “cause marketing fails” listicles where we could all get a laugh out of brands attaching themselves to causes they had absolutely no business being affiliated with, just so they could try and signal a higher purpose. Kentucky Fried Chicken’s buckets for the cure for breast cancer, Fleshlight’s celebration of the heroes of 9/11, and Pepsi’s infamous Kendall Jenner debacle come to mind.
Today, however, the green shoots of a new era are emerging as CSR is rapidly being productized and sold back to consumers as “D2C anti-capitalism.” In D2C anti-capitalism, solutions to the societal and environmental problems generated by capitalism are being sold back to consumers as products for purchase. Levi’s, Oatly, and Viking Cruises are standout examples, each expressing a different aspect of D2C anti-capitalism.
Levi’s
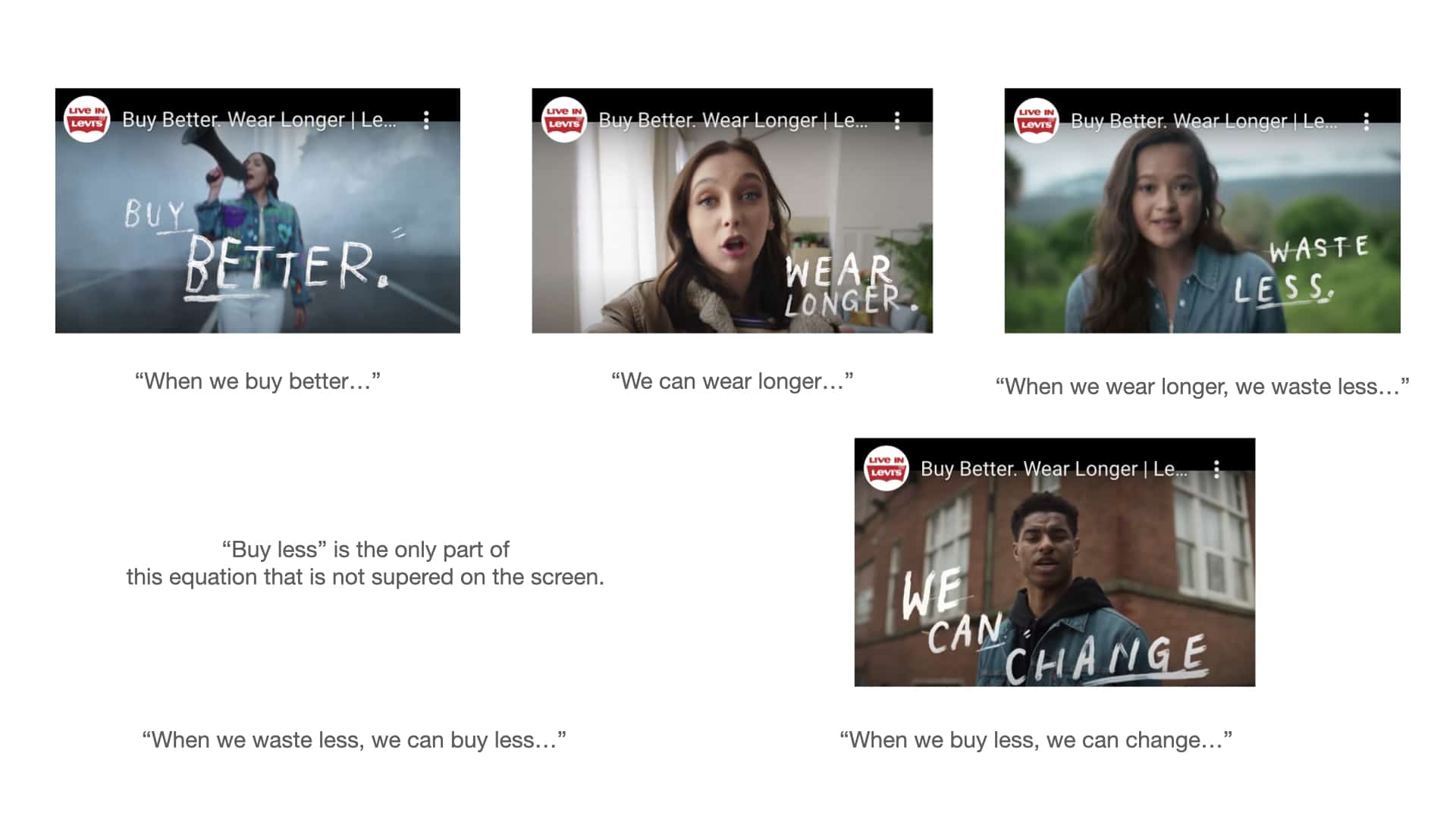
“When we buy better, we can wear longer. When we wear longer, we can waste less. When we waste less, we can buy less. When we buy less, we can change the world.” Notice the shift in emphasis here. Rather than Levi’s raising awareness for their CSR initiatives, the brand is inviting consumers to take charge and be the solution themselves. So the next time someone purchases a pair of 501’s, they’re given permission to feel like a forward thinking change agent helping end the scourge of fast-fashion and better the planet.
Oatly

Oatly has consistently fashioned itself as the anti-corporation, corporation. They know we know all about “washing,” so they’re explicit about not even trying to go there. Oatly is saying to consumers, “Hey, look, we get it. You’re tired of being lied to and sold to, so we’re not going to try and manipulate you and sell to you. We’re going to be self-deprecating so we’re in on the laugh with you.” Oatly knows how cynical modern consumers are, and how jaded we’ve all become by the overt sale in our nascent era of relatability. Anti, then, is their strategy.
Oatly has truly doubled down on this form of D2C anti-capitalism. Their widely panned 2021 super bowl ad set out to fail. They wanted to be annoying. They wanted to be a failure. They knew we would hate it, so they were ready to sell us T-Shirts that said “I totally hated that Oatly Super Bowl commercial.” Oatly has clearly imbibed Oscar Wilde’s famous adage that “the only thing worse than being talked about is not being talked about.”
Yet it’s difficult to deny their appeal. The anti-corporation corporation has been a runaway success. Oatly has established a fervent cult following – replete with merchandise – while becoming the oat milk of choice at Starbucks.
Viking Cruises

Viking Cruises, like Levi’s, is inviting consumers to become part of the solution to the climate crisis. Viking has recently begun to market their new Arctic “expeditions” as “vital planet saving research and discovery.” Their new Arctic ship is chock full of scientific activities that enable cruisers to feel like they’re actively helping to solve the climate crisis. Cruisers collect water samples, measure ocean acidification, analyze specimens under microscopes, and make personal climate pledges – all on multi-thousand dollar vacations with astronomical carbon footprints. With this move, Viking is selling the feeling of climate contribution.
Beatniks in The Boardroom: The Growth of Shareholder Activism
D2C anti-capitalism is a natural outgrowth of major shifts in CSR. Shareholder activism and social pressures have caused the scope of CSR to continually widen to encompass more and more issues that previously fell outside the remit of business. By April 2022, 576 proposals concerning social and environmental issues had been filed by investors, which is already up from the 499 filed in all of 2021. Proposals on environmental issues specifically are up 42% year-over-year in 2022. Shareholder proposals aimed at social and racial equity are also up in 2022.
The Economist has called annual shareholder meetings the new frontline in the battle for corporate purpose. Together with D2C anti-capitalism, shareholder activism reveals a growing understanding of the power of business to produce social outcomes, desirable or otherwise.
Clearly, this is a marked shift. In the 19th century, economists coined the term ‘externalities’ to describe how business imposes unpaid costs on society. Until recently, externalities tended mostly to be environmental pollutants. But the rise of an ever diversifying set of investor proposals reveals that shareholders (and society) are beginning to see racial injustice, economic inequality, and LGBTQ+ rights as externalities, as costs imposed on society by conducting business as usual.
Engine1 is an investment firm designed to hold businesses accountable for the total value of their impact on society. Engine1 pools investors together to buy corporate shares and then engage in shareholder activism. Their “total value framework” is meant to align economic value with positive social value. Engine1 is attempting to put a dollar value on the total impact a company has in order to give capital allocators and financial analysts a new way to value companies.
What’s new here is that previous activist firms have decided not to own shares of the most offending companies, but Engine1 believes you don’t run from the fire. Instead, you try to create positive social value from within.
Why This? Why Now?
“It’s easier to imagine the end of the world than to imagine the end of capitalism.”
Fredric Jameson, Political Theorist
Consumers today are the most educated they have ever been. The average consumer increasingly understands the connections between capitalism, culture, society, and individual psychology.
Let’s wade for a moment into the tensions the average college educated consumer reckons with these days. They want to go to the grocery store and be guaranteed to find fresh scallops, avocados and tomatoes at any time of year, no matter the location, even though they know it’s not natural or very good for the planet. They want to deepen their engagement with the world through travel, even though they’re aware of the climate costs (unless you’re cruising Viking). They want an iphone while also knowing Apple has questionable labor and environmental practices, and the jury is still out on the whole data privacy thing, too. And they’ve grown accustomed to cheap and immediate delivery from Amazon while knowing its workers are injured at a rate double that of other companies.
D2C anti-capitalism offers a way out of these tensions through the assuaging salvation it promises. And shareholder activism tries to get business to account for its effect on society. Yet still, these are half-measures, and consumers are feeling stagnant and ineffectual.
Generational nihilism has been proffered as a catchall descriptor of the malaise Americans feel today. It’s not exactly the classic “smoke em if you got em because we’re all going down so who really cares” brand of nihilism, though. It’s something else.
In a fascinating 2021 article called “How Nothingness Became Everything We Wanted” in the New York Times, Kyle Chayka asserts that “numbness beckons when life is difficult, when problems seem insurmountable, when there is so much to mourn.” Indeed, such widespread feelings of ineffectuality are exactly what D2C anti-capitalism is soothing.
Our problems do seem insurmountable, like we can’t do anything to fix society. That no one can. And social inequalities, the isolation of Covid-19, rancorous racial tumult, inescapable gun violence, and the ever-present titillations of partisan outrage porn that drive the click economy have combined to give us a lot to mourn. Lacking the ability to create real change, it makes sense that consumers are buying productized solutions to social problems. And it makes sense that activist investors continue to expand the horizons of corporate social responsibility.
D2C Anti-Capitalism: Future Force or Fleeting Fad?
At Concept Bureau, we focus on outlying signals of change that provide clues about the possible direction of our cultural and social futures. A central notion of futurists is that the “future is already here, it’s just not evenly distributed.” With that, the question then becomes, is the emergence of D2C anti-capitalism a signal of the future of CSR and branding? Or, will it be a passing fad, replaced by other, stronger signals of the future?
If we agree that D2C anti-capitalism is a reaction to our current cultural malaise in which Americans feel ineffectual and lack the agency necessary to create change, it’s reasonable to assume that, so long as the current cultural climate remains, the appeal of anti-capitalist branding will remain as well.
However, a growing chorus of cultural commentators are signaling that a vibe shift is underway.
The concept of the “vibe shift” is meant to capture cultural change, i.e. changes to the values that guide cultural production and the expression of our individual identities. No doubt, while it’s easy to feel the vibe shift in American culture right now, the concept isn’t deep enough to capture the magnitude of change that is beginning to be set in motion. Rather, what’s happening today is more akin to plate tectonics – a tectonic shift versus a vibe shift – because it’s happening at the level of our foundational institutions.
It’s not hyperbole to assert that over the next two decades, society will massively reinvent and reground itself on a different set of priorities from those of the past.
In this world, the personal agency to create what comes next is the highest form of cultural value. Indeed, people are already creating the worlds they want to live in – they’re “being the change they want to see in the world” as the Dalai Lama has famously put it. Let’s look at some examples of future signals that bear this direction out:
- The rise and diversification of ideological communities that essentially opt out of mass, global, and universal society in favor of more ancient, tribal modes of living amongst like-minded individuals. Such as parrothead retirements, anti-vax “Burning Man” utopias, Central American crypto cities, and micronations.
- The Great Resignation has large numbers of people leaving jobs in which they feel like cogs for jobs that are more personally meaningful. According to Google data, eight of the top ten most searched “how to become” jobs in 2021 were all jobs that provide ample amounts of agency and control: therapist, electrician, real estate agent, personal trainer, psychiatrist, firefighter, and pilot. These are jobs rich in human skill.
- The growing normalization of polyamory, open relationships and thruples signals an agentic reclamation of relationships, one that puts individual people, rather than social marriage norms, in control. Vogue reports that 22% of couples are already experimenting with various forms of consensual non-monogamy.
- The current explosion of interest in psychedelics, meditation (tripled in the U.S.A. since 2012), and Eastern spirituality loudly signals a desire to control our minds and “let in” things that were taboo for Americans in earlier eras. It’s hard to see these trends as anything other than agentic reclamations of holistic wellness and mental health.
- The astonishingly fast rise of cryptocurrency, DAO’s, and NFT’s suggests a desire for newfound collective control amidst the collapse of trust in old institutions.
- The rise of homeschooling, along with ideological attacks on public schools more generally, suggest a desire for tighter, more homogeneous communities. The rate of homeschooling shot up 63% in 2020, before only falling 17% from there in 2021.
Taken together, these signals point toward a future that is more decentralized, more ideological-collectivist and tribal, and less coherent and unified. In short, we’re using agency to create the worlds we want to live in, within “the current thing,” as Marc Andreessen has put it.
That world is being built today, it’s just not evenly distributed yet.
What Defines Brand Success In This Future?
D2C anti-capitalism exists today because it’s a soothing assuagement of the symptoms of social sickness, chiefly an ineffectual lack of personal agency.
CSR has gone from vision to product to enabling consumers to feel like they are a part of the solutions they’re seeking, and for which they have no recourse otherwise. Yet as the outlying future signals above suggest, individuals who are the most enlivened with agency today are using that power to create new social formations founded on different values: decentralization and community.
There are three main ways for brands to succeed in this future:
1. Be a Co-Creator of The Future Along With Your Customers
Are you in a category that can credibly help create what comes next? If so, lean into the restlessness of the moment and do all you can to signal you’re a co-creator of the future. Your values and brand actions are essential in this capacity. They’re what will signal to fellow change agents that you’re a brand on their side. That you, too, desire new social formations founded on the emerging values of decentralization and community. The worst thing your brand can do is signal that you’re anchored to the here and now, to the way things are today. To do that is to risk your customers moving into their futures without you.
2. Enable People To Create Their Future
If your brand is not in a future creation category, that’s okay. You can still enable people to pursue new worlds themselves, you just have to pick a lane – which is to say a community – and support them in the future they’re building. Your brand can’t be for everybody, so figure out the future vision that your people want. Then, do everything you can with your branding, messaging, and thought leadership to help your community of people bring their better future into being. This means having a strong POV and culturally resonate narratives that allow your customers to use your brand as a signal of change, as a signpost of meaning in society.
3. Create Communities
It’s our strategic conviction at Concept Bureau that we’ve left the era of weak ties and entered the era of strong ties in which communities are the new brands. Any brand is capable of creating new communities, or nurturing and uplifting existing communities. The key here is to understand what those communities want, and how you can help achieve that with your brand actions. Communities have always been vehicles for agency and action, and this will only deepen in the possible future laid out here. If your brand can become a valued member of a community, you’ll lessen the risk that your brand won’t be participating in that future horizon with them.
People can remain mired in nihilism, but societies never do, especially not dynamic capitalist societies. The winning brands of the next decade will be ones that first understand the emotional and cultural currents that are pulling people into their futures, and then armed with that knowledge, help them sprint toward it.




