You can’t move the market if you don’t know how to read the market.
There’s a big difference between building a brand for today and building a strategic brand for the horizon of your industry.
I meet a lot of branding people who create or consult companies based on two-dimensional principles. That usually sounds something like:
- “We’re making health food for the young urban professional that doesn’t have time to cook, but wants to feel good about what’s going into their body.”
- “We’re a D2C lifestyle clothing brand for young, single men who aren’t afraid to put some personality in their wardrobes.”
- “Our brand is for the millennial yoga mom who wants an electric car that reflects her values.”
- “We provide frictionless financial solutions for small businesses and their vendors.”
If any of these sound familiar, then you are building a brand for the here-and-now. It will work for the here-and-now, but there is no strategy for how it will compete in the next few years.
That’s because these brands fail to look at the deep signals that are going to move their markets. Some of the most important of these signals are in culture and definitions, and it takes a keen understanding of markets and mentalities in order to pick up on them.
They are hidden because they haven’t emerged yet, but the groundwork for what they will mean to us as consumers is already being laid.
This is part of thinking like a brand strategist. I’ve written about it in a previous post, but here I want to cut deeper into a certain aspect of what those signals mean and where to find them. Specifically, the more foundational signals we may take for granted but see all around us in the world.
Above all, I want us to explore how to use these signals for your own brand. If you’re creating a brand based on strategy, it’s important to have a curiosity not only for how things are changing, but why, and to apply that ‘why’ to your own business.
You’ll see that these signals can come from any corner of the playing field, and yet can be applied to nearly any business in the landscape.
Signals usually supersede any particular vertical because they’re not about the market itself, but rather the forces that move the market forward.
You can’t move the market if you don’t know how to read the market.
Once you see a signal, you start to understand how it powers much of the activity in our lives.
Signals are codes. They underlie what you see on the surface of a market, and the strongest brands out there have made those codes part of their DNA.
Collective Culture
A strategist has to be something of a cultural anthropologist. You have to see your users as individuals as well as products of their surroundings and part of a greater whole.
Sometimes, a glitch in the cultural system can lead you to the faulty code of a signal. I saw something like this recently in an old story about finance.
The world’s first index fund was founded by John Bogle of The Vanguard Group in 1975. There was nothing like it at the time. You couldn’t simply ‘invest in the market’, and most investors worked with advisors to actually beat the market with their portfolios.
The entire investment paradigm at that time was to perform better by placing your bets in a subset of market stocks.
Bogle, however, noticed something interesting that was starting to emerge in the research of economists like Paul Samuelson and Burton Malkiel.
He saw that oftentimes, if you just invested in a weighted basket of all stocks in the market, you’d be better off than trying to beat the market by predicting with a few key companies. In other words, the average of the market performed better than most investors did with their portfolios… and he had the historical figures to prove it.
That sounds logical, right?
But for many it wasn’t. The concept of an index fund was met with huge resistance in the financial community, as well as its fair share of ridicule.
It was called “un-American” and Fidelity Investments Chairman Edward Johnson was quoted as saying that he “[couldn’t] believe that the great mass of investors are going to be satisfied with receiving just average returns”.
An executive from a different firm wrote that all but “a very small minority” believe “index funds are a ‘cop-out’ and a fad that will soon disappear.”
That should draw your attention.
Why would Americans believe, that despite all the logic and proof behind it, an index fund was un-American and destined to fail?
Because there is something about being American that stands in the face of what Bogle’s fund represented.
It’s a sin to be average in America.
Somewhere, deep in our collective psyche, we believe that to be American means to be exceptional, and that cultural quirk revealed itself back in 1975 in this very incident.

It’s such a sin to be average in America, that we are willing to ignore facts and figures in order to prove our beliefs.
How to use this signal.
As a brand, you can use this signal for your own benefit.
There are themes of exceptionalism, elitism, superiority, personal potential and self-discovery all wrapped up in this signal. These are strong personal motivators, whether we admit them or not.
That’s why stories like The Ugly Duckling keep recurring over and over again in the canon in modern day versions like John Snow in Game of Thrones and (of course) Harry Potter.
At the root of it, there’s an interesting mentality.
This is about changing your perception of yourself.
We can’t change the story that it’s a sin to be average, but we can change the average.
Changing the context can change user perceptions.
As a business, you can take what is normal about a user and reposition it as something extraordinary.
Brands like Moleskin, Apple and Bulletproof Coffee have all elevated something mundane about their users into something far more valuable.
That change in perceptions is the added value of their brands. When you use their products or buy into their philosophies, you are changing your perception of who you are.
Don’t underestimate the power of this mechanic. When perceptions shift, so does our purchasing.
[You can uncover other cultural signals using The Emergent Story Arc here.]
Changing Definitions
I’ve written before that peoples’ values rarely change, but the beliefs that sit on top of those values are more fluid and change easily.
Sometimes our very definitions even change.
We carry a big cultural value to eat what is good for us. But the definition of eating good food has evolved from the 1950’s through to today. Some of that was powered by science and government guidance, but a lot of it has been powered by beliefs around ethics, how we gather as a community, and what foods actually provide for our bodies.
The modern health food ‘craze’ as we know it today first took hold in the 80s and 90s, when restaurants like Souplantation and El Pollo Loco were rapidly growing.
Both of them reflected the healthy eating definitions of the time: that fresh food was healthy food. Souplantation had the mile-long buffet filled with trays of colorful produce. El Pollo Loco made open kitchens core to all of their locations and showed your flame broiled chicken being prepared, without microwaves or pre-processed ingredients, right in front of you.
By 2014, El Pollo Loco had taken on considerable debt and losses (despite growth), and since going public in that same year, the stock price has steadily declined by 40%.
By the 2017, Souplantation had filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy.
The decline in casual dining and overall declines in the market hit both companies hard. They weren’t mismanaged, but they were relics of a bygone era. Not because we stopped eating healthy, but because our definition of healthy had shifted.
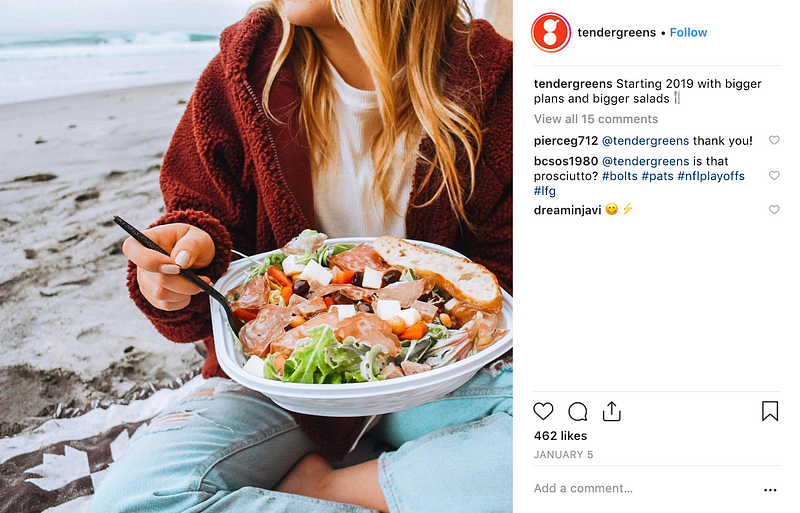
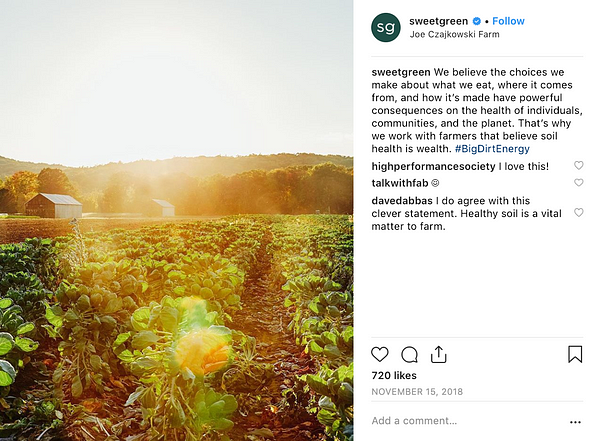
Meanwhile, new salad upstarts like Sweetgreen, Salata, Tender Greens and Chopt are booming because they were smart enough to tap into a new definition of eating healthy.
They saw that it wasn’t just about the food anymore, but about sustainable practices, transparency about where the food comes from and the artisanal craft of preparing and honoring that food.
Sweetgreen made a point of teaching consumers that, unlike places like El Pollo Loco and Souplantation, people should not expect to get the same standard of food in every restaurant location:
“We want people to understand that that’s normal and that’s okay,” [Sweetgreen’s co-founder Nathaniel Ru says. “Something should taste different in a different place.”
That’s a major shift away from traditional fast-food principles, which dictate that customers should be able to walk into any location and get the exact same food and experience. In this realm, each chain is constantly trying to prove it’s more connected to farmers than the other guy. (Fresh&Co even bought its own farm on Long Island, announcing it would provide “hyper-local seasonal” ingredients.)
These brands understood that our definition of eating good went from ‘food that looks fresh’ to ‘food that has a story’.
How to use this signal.
Definitions are a different kind of signal. When definitions change, it’s a reevaluation of our beliefs, but also a recommitment to our values.
Definitions, above all, need to be spelled out.
If, as a brand, you see that your audience is starting to untether themselves from a belief that centers around a core value, that’s a tremendous opportunity to help people define that change.
When consumers start to feel a change in their beliefs, it’s the brands who define those changes that win.
You can help people change the definitions around them, when they’re ready, by giving them a concrete stepping stone for getting there.
We didn’t know that we wanted to play with our makeup until Glossier defined that new relationship for us, although young women were starting to feel it.
We didn’t consciously realize that our cars were turning from self-expressive statements to utilitarian objects, but SUVs got us there. That’s why sedans have started to fade away and SUVs, the fastest growing truck category, have increased in shares to 42%, from 30% in 2010.
If you watch carefully, you will see a changing definition in your own industry (if not a few).
You can help people articulate it and become an important part of your user’s evolution into a new set of beliefs.
There’s always a signal.
I’ve seen that even in the stalest of industries, where it may seem as if there’s no innovation and no change in what consumers are searching for, there is, in fact, a signal.
It may be weak, but it’s there. Nothing in the market is static, and nothing about your audience is set in stone.
If you search for that emerging change, you will find it. Building a strategic brand means digging for those signals and making them a part of your DNA.




